Tootekategooriad
- termiline kaitse 32
- pinnale kinnitatavad kaitsmed 12
- termistor 36
- PCB kinnitus kaitsme hoidik 27
- Juhtmestik 6
- Tera kaitsmehoidjad 17
- termostaat 50
- Elektri kaitsme 24
- Autotemperatuuri andur 7
- Soojuslüliti 22
- Kaitsmekastihoidja 36
- Temperatuuriandur 75
- Termiline lüliti 68
- Autokaitsja 20
- Kinnitage kaitsmed 8
Tootesildid
Komposiit-PTC-termistor transformaatoritele, Lülitusvõimsus
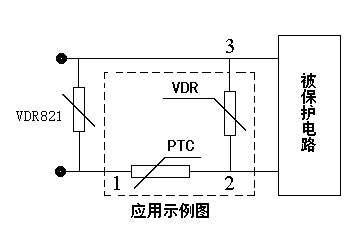
Komposiit-PTC-termistor kasutab termiliselt ühendatud kombinatsiooni, VDR-varistori ja PTC-termistori tihedalt sobitamine ja kapseldamine. Seda kasutatakse peamiselt toiteallikate ja trafo primaarahelate lülitamisel võimsusmõõturites ja muudes toiteallikates, pakkudes igakülgset voolu- ja pingekaitset.
A composite PTC thermistor is an electronic component that combines positive temperature coefficient (PTC) characteristics with overvoltage protection, primarily used for dual overcurrent and overvoltage protection. Komposiit-PTC-termistor kasutab termiliselt ühendatud kombinatsiooni, VDR-varistori ja PTC-termistori tihedalt sobitamine ja kapseldamine. Seda kasutatakse peamiselt toiteallikate ja trafo primaarahelate lülitamisel võimsusmõõturites ja muudes toiteallikates, pakkudes igakülgset voolu- ja pingekaitset. This solves the difficulties associated with using a single PTC thermistor with transformers. Instruments and equipment protected by a PTC thermistor may not function properly under overvoltage or overcurrent conditions, and low-temperature instruments may not be protected by the PTC when abnormalities occur.
The following is an analysis of its core features and applications:
I. Structure and Principle
Material Composition: Typically made from a polyolefin resin, polyethylene, or epoxy resin matrix, conductive particles such as carbon black and vanadium oxide are incorporated. Toatemperatuuril, the conductive particles form continuous conductive chains, resulting in low resistivity. When the temperature rises to the polymer melting point, the matrix expands, breaking the conductive chains and causing a sudden increase in resistivity (PTC effect). Composite Design: Some models integrate a PTC thermistor and a varistor (VDR) into a single package, achieving dual overcurrent and overvoltage protection through thermal coupling. Näiteks, during an overvoltage event, the varistor absorbs energy and generates heat, triggering a jump in the PTC’s resistance, limiting current and reducing voltage by 4%.
II. Performance Characteristics
RISE-TO-RESISTANCE RATIO: The resistance can vary by 5-10 orders of magnitude within a narrow temperature range, making it suitable as a thermal switch element.
RESPONSIBILITY: After actuation, it takes a long time to cool down before returning to its initial state, resulting in a slow response.
SELF-RECOVERY: Automatically returns to a low-resistance state after the fault is resolved, eliminating the need for replacement.
III. Typical Applications
Home Appliances and Industrial: Used for overcurrent protection in equipment such as electric water heaters, mootorid, ja trafod.
Power Meters: Provides combined overvoltage and overcurrent protection in smart meters and switching power supplies.
Autoelektroonika: Used in temperature monitoring applications such as engine control and air conditioning systems.
When a varistor absorbs large amounts of energy, it will heat up. Due to thermal coupling, the temperature of the PTC thermistor also rises. Furthermore, the thermistor itself heats up due to the increased current. When the temperature reaches the PTC thermistor’s switching temperature, its resistance jumps, and the current decreases sharply. Simultaneously, the voltage drop across the thermistor increases significantly, reducing the voltage across the varistor and allowing only a small leakage current to flow. This reduces the voltage of the protected circuit to within the normal operating voltage range, allowing the power meter to operate normally.
IV. Selection Parameters
The following parameters should be considered during selection:
Operating current (It) and non-operating current (Ih);
Curie temperature (Tc, typically 115±7°C);
Varistor voltage (V) and maximum operating voltage (Vmax).
Common models of composite thermistors
| Mudel | Curie | Actuating | Non-Actuating | Varisor | Hinnang | Mõõtmed | |
| Temperatuur | Praegune | Praegune | Pinge | Maximum Operating | |||
| (25℃) | (60℃) | (25℃) | Pinge | ||||
| Tc(℃) | It(mA) | Ih(mA) | V(V) | Vmax(V) | Dmax | Hmax | |
| SPMZB-10S300-500RM/14D900 | 115±7 | 250 | 70 | 90 | 65 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S300-600RM/14D121 | 115±7 | 200 | 60 | 120 | 65 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S400-800RM/14D181 | 115±7 | 200 | 50 | 180 | 120 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-10S300-500RM/14D181 | 115±7 | 250 | 70 | 180 | 120 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-06S900-161RM/10D391 | 115±7 | 150 | 30 | 390 | 265 | 12 | 8 |
| SPMZB-06S151-251RM/10D391 | 115±7 | 120 | 25 | 390 | 265 | 12 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S400-800RM/12D391 | 115±7 | 200 | 50 | 390 | 265 | 14 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S600-121RM/12D391 | 115±7 | 180 | 40 | 390 | 265 | 14 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S600-121RM/14D391 | 115±7 | 180 | 40 | 390 | 265 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S800-161RM/14D391 | 115±7 | 160 | 35 | 390 | 265 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-10S300-500RM/14D391 | 115±7 | 250 | 90 | 390 | 265 | 16 | 10 |
| SPMZB-10S400-800RM/14D391 | 115±7 | 220 | 70 | 390 | 265 | 16 | 10 |
| SPMZB-10S400-800RM/14D471 | 115±7 | 220 | 70 | 470 | 330 | 16 | 10 |
| SPMZB-16S200-300RM/20D391 | 115±7 | 450 | 130 | 390 | 265 | 22 | 10 |
Võtke meiega ühendust
Ootan teie meili, vastame teile sees 12 tundi väärtusliku teabega, mida vajate.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt