مزاحم درجہ حرارت کا پتہ لگانے والے یا آر ٹی ڈی درجہ حرارت کے سینسر کی سادہ قسم کی قسم ہوسکتی ہے. یہ آلات اس اصول پر کام کرتے ہیں کہ درجہ حرارت کے ساتھ دھات کی مزاحمت بدل جاتی ہے. خالص دھاتوں میں عام طور پر مزاحمت کا ایک مثبت درجہ حرارت کا گتانک ہوتا ہے, اس کا مطلب ہے کہ درجہ حرارت میں اضافہ ہوتے ہی ان کی مزاحمت میں اضافہ ہوتا ہے. RTDs وسیع درجہ حرارت کی حد سے زیادہ کام کرتے ہیں -200 ° C سے +850 ° C اور اعلی درستگی کی پیش کش کریں, بہترین طویل مدتی استحکام, اور دہرانے کے قابل.
اس مضمون میں, ہم آر ٹی ڈی کے استعمال کے تجارتی تعلقات پر تبادلہ خیال کریں گے, ان میں استعمال ہونے والی دھاتیں, آر ٹی ڈی کی دو اقسام, اور آر ٹی ڈی کس طرح تھرموکوپلس سے موازنہ کرتے ہیں.
اس سے پہلے کہ ہم ڈوبکی, آئیے RTD کی بنیادی باتوں کو بہتر طور پر سمجھنے کے لئے ایک مثال کے طور پر ایپلی کیشن آریگرام پر ایک نظر ڈالتے ہیں.
RTD ایپلی کیشن ڈایاگرام مثال
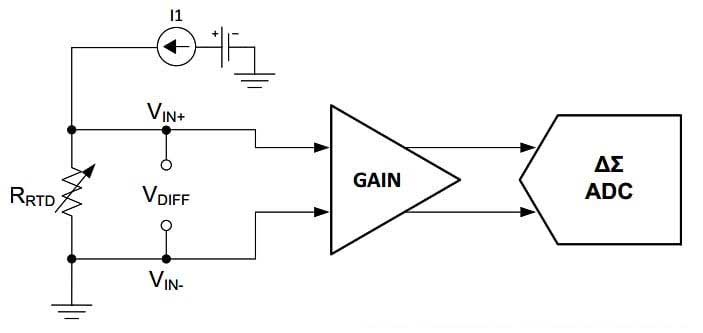
آر ٹی ڈی غیر فعال ڈیوائسز ہیں جو خود ہی آؤٹ پٹ سگنل پیدا نہیں کرتے ہیں. اعداد و شمار 1 ایک آسان RTD ایپلی کیشن ڈایاگرام دکھاتا ہے.
اعداد و شمار 1. RTD ایپلی کیشن ڈایاگرام مثال.
جوش و خروش موجودہ I1 سینسر کی درجہ حرارت پر منحصر مزاحمت سے گزرتا ہے. یہ ایک وولٹیج سگنل پیدا کرتا ہے جو جوش و خروش کے موجودہ اور RTD کی مزاحمت کے متناسب ہے. پھر RTD کے اس پار وولٹیج کو بڑھاوا دیا جاتا ہے اور ADC کو بھیجا جاتا ہے (ینالاگ سے ڈیجیٹل کنورٹر) ڈیجیٹل آؤٹ پٹ کوڈ تیار کرنے کے لئے جو RTD درجہ حرارت کا حساب لگانے کے لئے استعمال کیا جاسکتا ہے.
RTD سینسر کے استعمال کے تجارتی عمل - RTD سینسروں کے فوائد اور نقصانات
اس سے پہلے کہ ہم ڈوبکی, یہ نوٹ کرنا ضروری ہے کہ آر ٹی ڈی سگنل کنڈیشنگ کی تفصیلات مستقبل کے مضمون میں شامل ہوں گی. اس مضمون کے لئے, میں RTD سرکٹس کا استعمال کرتے وقت کچھ بنیادی تجارت کو اجاگر کرنا چاہتا ہوں.
پہلے, نوٹ کریں کہ جوش و خروش موجودہ عام طور پر آس پاس تک محدود ہے 1 ایم اے خود گرمی کے اثرات کو کم سے کم کرنے کے لئے. جب جوش و خروش موجودہ RTD کے ذریعے بہتا ہے, یہ I2R یا جولائی ہیٹنگ پیدا کرتا ہے. خود گرم ہونے والے اثرات سینسر کے درجہ حرارت کو محیطی درجہ حرارت سے بالاتر قدروں میں بڑھا سکتے ہیں جو حقیقت میں ماپا جارہا ہے. جوش و خروش کو کم کرنے سے خود گرمی کا اثر کم ہوسکتا ہے. یہ بات بھی قابل ذکر ہے کہ خود گرمی کا اثر اس میڈیم پر منحصر ہوتا ہے جس میں آر ٹی ڈی ڈوب جاتا ہے. مثال کے طور پر, an RTD placed in still air may experience more significant self-heating effects than an RTD immersed in flowing water.
For a given detectable temperature change, the change in RTD voltage should be large enough to overcome system noise as well as offsets and drifts of different system parameters. Since self-heating limits the excitation current, we need to use an RTD with a large enough resistance, thus generating a large voltage for the downstream signal processing block. While a large RTD resistance is desirable to reduce measurement errors, we cannot arbitrarily increase the resistance because a larger RTD resistance results in a slower response time.
RTD Metals: Differences Between Platinum, Gold, and Copper RTDs
In theory, any kind of metal can be used to construct an RTD. The first RTD invented by CW Siemens in 1860 used a copper wire. تاہم, Siemens soon discovered that platinum RTDs produced more accurate results over a wider temperature range.
آج, platinum RTDs are the most widely used temperature sensors for precision temperature measurement. Platinum has a linear resistance-temperature relationship and is highly repeatable over a large temperature range. اس کے علاوہ, platinum does not react with most pollutant gases in the air.
In addition to platinum, two other common RTD materials are nickel and copper. جدول 1 provides the temperature coefficients and relative conductivity of some common RTD metals.
جدول 1. Temperature coefficients and relative conductivity of common RTD metals. Data provided by BAPI
| Metals | Relative conductivity (copper = 100% @ 20 ° C) | Temperature coefficient of resistance |
| Annealed copper | 100% | 0.00393 Ω/Ω/°C |
| Gold | 65% | 0.0034 Ω/Ω/°C |
| Iron | 17.70% | 0.005 Ω/Ω/°C |
| نکل | 12-16% | 0.006 Ω/Ω/°C |
| پلاٹینم | 15% | 0.0039 Ω/Ω/°C |
| Silver | 106% | 0.0038 Ω/Ω/°C |
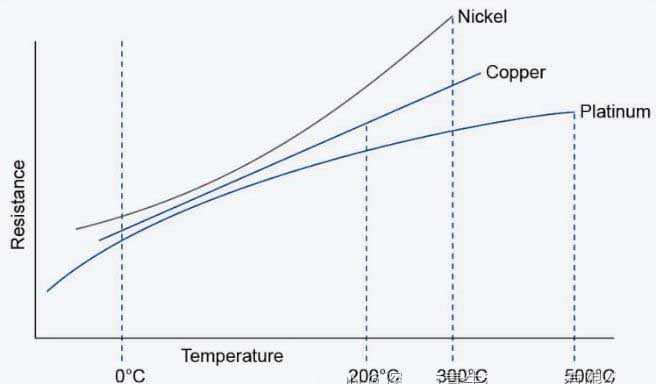
In the previous section, we discussed how larger RTD resistance can reduce measurement errors. Copper has a higher conductivity (or equivalently, lower resistance) than platinum and nickel. For a given sensor size and excitation current, a copper RTD can produce a relatively small voltage. لہذا, copper RTDs can be more challenging to measure small temperature changes. اس کے علاوہ, copper oxidizes at higher temperatures, so the measurement range is also limited to -200 to +260 ° C. Despite these limitations, copper is still used in some applications due to its linearity and low cost. As shown in Figure 2 below, of the three common RTD metals, تانبے میں سب سے زیادہ لکیری مزاحمت درجہ حرارت کی خصوصیت ہے.
اعداد و شمار 2. مزاحمت بمقابلہ. نکل کی درجہ حرارت کی خصوصیات, تانبے, اور پلاٹینم آر ٹی ڈی. تصویر بشکریہ ٹی ای رابطے کی
سونے اور چاندی کی بھی نسبتا low کم مزاحمت ہوتی ہے اور شاذ و نادر ہی RTD عناصر کے طور پر استعمال ہوتا ہے. نکل کے پاس پلاٹینم کے قریب چالکتا ہے. جیسا کہ اعداد و شمار میں دیکھا جاسکتا ہے 2, نکل درجہ حرارت میں دی گئی تبدیلی کے لئے مزاحمت میں تبدیلی پیش کرتا ہے.
تاہم, نکل درجہ حرارت کی کم حد پیش کرتا ہے, زیادہ سے زیادہ عدم استحکام, اور پلاٹینم سے زیادہ طویل مدتی بہاؤ. اضافی طور پر, نکل کی مزاحمت بیچ سے بیچ تک مختلف ہوتی ہے. ان حدود کی وجہ سے, نکل بنیادی طور پر کم لاگت والی ایپلی کیشنز جیسے صارفین کی مصنوعات میں استعمال ہوتا ہے.
عام پلاٹینم آر ٹی ڈی PT100 اور PT1000 ہیں. یہ نام سینسر کی تعمیر میں استعمال ہونے والی دھات کی قسم کی وضاحت کرتے ہیں (پلاٹینم یا پی ٹی) اور برائے نام مزاحمت 0 ° C, جو ہے 100 pt PT100 اور کے لئے 1000 P PT100 اور PT1000 اقسام کے لئے, بالترتیب. ماضی میں PT100 کی اقسام زیادہ مقبول تھیں; تاہم, آج یہ رجحان اعلی مزاحمت آر ٹی ڈی کی طرف ہے, چونکہ اعلی مزاحمت بہت کم یا کوئی اضافی قیمت پر زیادہ حساسیت اور قرارداد فراہم کرتی ہے. تانبے اور نکل سے بنی آر ٹی ڈی اسی طرح کے نام کے کنونشنوں کا استعمال کرتی ہیں. جدول 2 کچھ عام اقسام کی فہرست دیتا ہے.
جدول 2. RTD اقسام, مواد, اور درجہ حرارت کی حدود. ینالاگ آلات کے ذریعہ فراہم کردہ ڈیٹا
| تھرمل ریزسٹر کی قسم | مواد | حد |
| PT100, PT1000 | پلاٹینم (نمبر پر مزاحمت ہیں 0 ° C) | -200 ° C سے +850 ° C |
| PT200, PT500 | پلاٹینم (نمبر پر مزاحمت ہیں 0 ° C) | -200 ° C سے +850 ° C |
| Cu10, Cu100 | تانبے (نمبر پر مزاحمت ہیں 0 ° C) | -100 ° C سے +260 ° C |
| نکل 120 | نکل (نمبر پر مزاحمت ہیں 0 ° C) | -80 ° C سے +260 ° C |
استعمال شدہ دھات کی قسم کے علاوہ, آر ٹی ڈی کا مکینیکل ڈھانچہ سینسر کی کارکردگی کو بھی متاثر کرتا ہے. آر ٹی ڈی کو دو بنیادی اقسام میں تقسیم کیا جاسکتا ہے: پتلی فلم اور وائر وونڈ. ان دونوں اقسام پر مندرجہ ذیل حصوں میں تبادلہ خیال کیا جائے گا.
پتلی فلم بمقابلہ. وائر واؤنڈ آر ٹی ڈی
آر ٹی ڈی کے بارے میں ہماری گفتگو کو مزید آگے بڑھانے کے لئے, آئیے دو اقسام کی تلاش کریں: پتلی فلم اور وائر وونڈ.
پتلی فلم RTD بنیادی باتیں
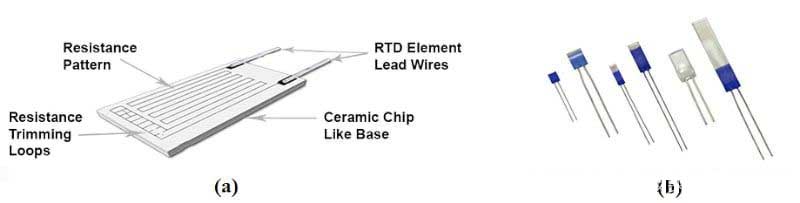
پتلی فلم کی قسم کا ڈھانچہ اعداد و شمار میں دکھایا گیا ہے 3(a).
اعداد و شمار 3. پتلی فلم آر ٹی ڈی کی مثالیں, جہاں (a) ساخت اور ظاہر کرتا ہے (بی) مختلف مجموعی اقسام کو ظاہر کرتا ہے. تصویر (ترمیم شدہ) بشکریہ ایوسینسرز
ایک پتلی فلم RTD میں, پلاٹینم کی ایک پتلی پرت سیرامک سبسٹریٹ پر جمع کی جاتی ہے. اس کے بعد بہت زیادہ درجہ حرارت اینیلنگ اور استحکام ہوتا ہے, اور ایک پتلی حفاظتی شیشے کی پرت جو پورے عنصر کو ڈھک جاتی ہے. تراشنے والا علاقہ اعداد و شمار میں دکھایا گیا ہے 3(a) تیار کردہ مزاحمت کو کسی مخصوص ہدف کی قیمت میں ایڈجسٹ کرنے کے لئے استعمال کیا جاتا ہے.
Thin film RTDs rely on relatively new technology that significantly reduces assembly time and production costs. Compared to the wirewound type, which we will explore in depth in the next section, thin film RTDs are more resistant to damage from shock or vibration. اضافی طور پر, thin-film RTDs can accommodate large resistances in a relatively small area. مثال کے طور پر, a 1.6 mm by 2.6 mm sensor provides enough area to produce a resistance of 1000 اوہ. Due to their small size, thin-film RTDs can respond quickly to temperature changes. These devices are suitable for many general-purpose applications. The disadvantages of this type are relatively poor long-term stability and a narrow temperature range.
وائر واؤنڈ آر ٹی ڈی
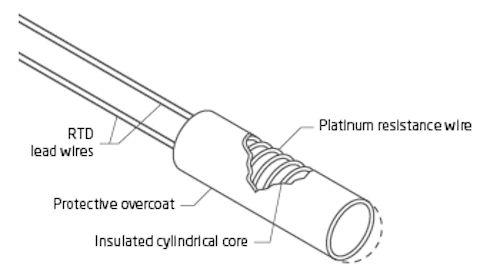
اعداد و شمار 4. Overview of the construction of a basic wirewound RTD. Image courtesy of PR Electronics
This type of RTD is made by winding a length of platinum around a ceramic or glass core. The entire element is usually encapsulated within a ceramic or glass tube for protection purposes. RTDs with ceramic cores are suitable for measuring very high temperatures. Wirewound RTDs are generally more accurate than thin-film types. تاہم, they are more expensive and more easily damaged by vibration.
To minimize any strain on the platinum wire, the thermal expansion coefficient of the material used in the sensor construction should match that of the platinum. Identical thermal expansion coefficients minimize resistance changes caused by long-term stress in the RTD element, thus improving sensor repeatability and stability.
RTD vs. Thermocouple Properties
To wrap up this conversation about RTD temperature sensors, here is a brief comparison between RTD and thermocouple sensors.
A thermocouple produces a voltage that is proportional to the temperature difference between its two junctions. Thermocouples are self-powered and do not require external excitation, whereas RTD-based temperature measurements require an excitation current or voltage. Thermocouple output specifies the temperature difference between the cold and hot junctions, so cold junction compensation is required in thermocouple applications. دوسری طرف, cold junction compensation is not required for RTD applications, resulting in a simpler measurement system.
Thermocouples are typically used in the -184 ° C سے 2300 °C range, while RTDs can measure from -200 ° C سے +850 ° C. Although RTDs are generally more accurate than thermocouples, they are approximately two to three times more expensive than thermocouples. Another difference is that RTDs are more linear than thermocouples and exhibit superior long-term stability. With thermocouples, chemical changes in the sensor material can reduce long-term stability and cause the sensor reading to drift.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt