A temperature acquisition circuit for a PT100 or PT1000 sensor probe typically consists of a stable current source to excite the sensor, a high-precision resistance measurement circuit to detect the change in resistance with temperature, and an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) to convert the measured voltage into a digital signal that can be processed by a microcontroller or data acquisition system; the key difference between a PT100 and PT1000 circuit is the scale of resistance values due to the Pt100 having a nominal resistance of 100 ohms at 0°C while a Pt1000 has 1000 omai 0 ° C., often requiring adjustments in the measurement circuit depending on the desired accuracy and application.
The article introduces the resistance change of PT100 and PT1000 metal thermal resistor sensor probes at different temperatures, as well as a variety of temperature acquisition circuit solutions. Including resistance voltage division, bridge measurement, constant current source and AD623, AD620 acquisition circuit. In order to resist interference, especially electromagnetic interference in the aerospace field, an airborne PT1000 temperature sensor acquisition circuit design is proposed, including a T-type filter for filtering and improving measurement accuracy.
Abstract generated by CSDN through intelligent technology
PT100/PT1000 temperatūros matavimo grandinės sprendimas
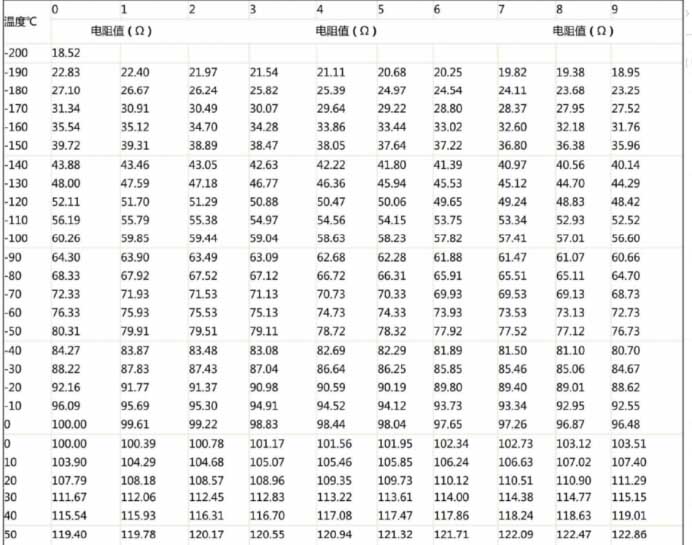
1. Temperature resistance change table of PT100 and PT1000 sensors
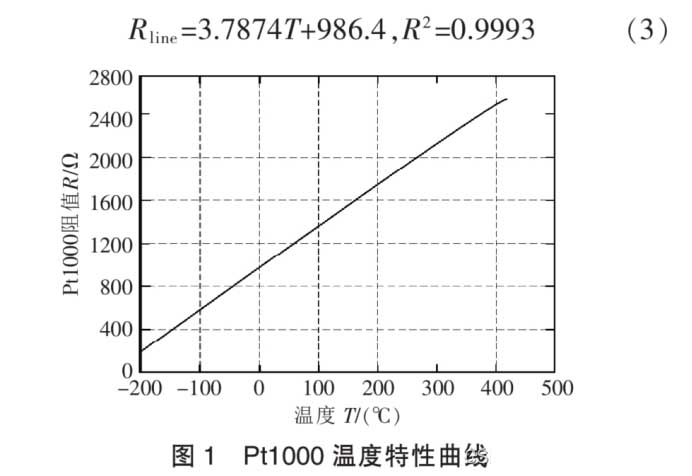
Metaliniai šiluminiai rezistoriai, tokie kaip nikelis, copper and platinum resistors have a positive correlation with the change of temperature. Platina turi stabiliausias fizines ir chemines savybes ir yra plačiausiai naudojama. Dažniausiai naudojamų platinos atsparumo Pt100 jutiklių zondų temperatūros matavimo diapazonas yra -200~850 ℃, ir temperatūros matavimo diapazonai Pt500, Pt1000 jutiklio zondai, ir tt. nuosekliai mažinami. 1000 Pt, temperatūros matavimo diapazonas yra -200 ~ 420 ℃. Pagal IEC751 tarptautinį standartą, platininio rezistoriaus Pt1000 temperatūros charakteristikos atitinka šiuos reikalavimus:
Pagal Pt1000 temperatūros charakteristikų kreivę, the slope of the resistance characteristic curve changes slightly within the normal operating temperature range (kaip parodyta paveiksle 1). The approximate relationship between resistance and temperature can be obtained through linear fitting:
2. Dažniausiai naudojami gavimo grandinių sprendimai
2. 1 Resistor voltage divider output 0~3.3V/3V analog voltage single chip AD port direct acquisition
Temperatūros matavimo grandinės įtampos išvesties diapazonas yra 0–3,3 V, PT1000 (PT1000 atsparumo vertė labai pasikeičia, and the temperature measurement sensitivity is higher than PT100; PT100 labiau tinka didelio masto temperatūros matavimams).
Paprasčiausias būdas yra naudoti įtampos padalijimo metodą. The voltage is generated by the TL431 voltage reference source chip, which is a 4V voltage reference source. Arba, REF3140 can be used to generate 4.096V as a reference source. Reference source chips also include REF3120, 3125, 3130, 3133, ir 3140. The chip uses a SOT-32 package and a 5V input voltage. Išėjimo įtampą galima pasirinkti pagal reikiamą atskaitos įtampą. Žinoma, according to the normal voltage input range of the AD port of the microcontroller, ji negali viršyti 3V/3,3V.
2.2 Resistor voltage division output 0~5V analog voltage, and the AD port of the microcontroller directly collects it.
Žinoma, some circuits are powered by a 5V microcontroller, and the maximum operating current of the PT1000 is 0.5mA, so an appropriate resistance value must be used to ensure the normal operation of the component.
Pavyzdžiui, the 3.3V in the voltage division schematic diagram above is replaced by 5V. The advantage of this is that the 5V voltage division is more sensitive than the 3.3V voltage, and the collection is more accurate. Prisimink, teorinė skaičiuojama išėjimo įtampa negali viršyti +5V. Priešingu atveju, the microcontroller will be damaged.
2.3 Dažniausiai naudojamas tilto matavimas
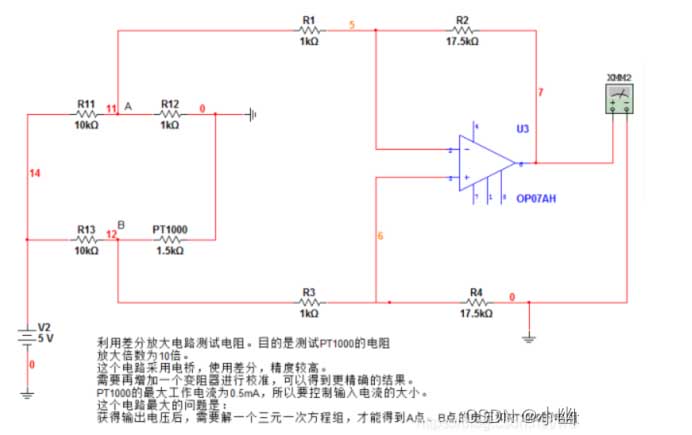
Use R11, R12, R13 and Pt1000 to form a measurement bridge, kur R11=R13=10k, R12=1000R precision resistor. Kai Pt1000 varžos vertė nėra lygi R12 varžos vertei, the bridge will output a mV level voltage difference signal. Šį įtampos skirtumo signalą sustiprina prietaiso stiprintuvo grandinė ir išvedamas norimas įtampos signalas, which can be directly connected to the AD conversion chip or the AD port of the microcontroller.
Šios grandinės varžos matavimo principas:
1) PT1000 yra termistorius, and its resistance changes basically linearly with the change of temperature.
2) At 0 laipsnių, PT1000 varža yra 1kΩ, tada Ub ir Ua yra lygūs, tai yra, Uba = Ub – Daryk = 0.
3) Darant prielaidą, kad esant tam tikrai temperatūrai, PT1000 varža yra 1,5 kΩ, tada Ub ir Ua nėra lygūs. According to the voltage divider principle, we can find Uba = Ub – Daryk > 0.
4) OP07 yra operacinis stiprintuvas, and its voltage amplification factor A depends on the external circuit, kur A = R2/R1 = 17.5.
5) OP07 išėjimo įtampa Uo = Uba * A. Taigi, jei naudosime voltmetrą OP07 išėjimo įtampai matuoti, galime daryti išvadą apie Uab vertę. Kadangi Ua yra žinoma reikšmė, galime toliau apskaičiuoti Ub reikšmę. Tada, using the voltage divider principle, galime apskaičiuoti specifinę PT1000 varžos vertę. Šis procesas gali būti atliktas naudojant programinės įrangos skaičiavimus.
6) Jei žinome PT1000 varžos vertę bet kurioje temperatūroje, we only need to look up the table according to the resistance value to know the current temperature.
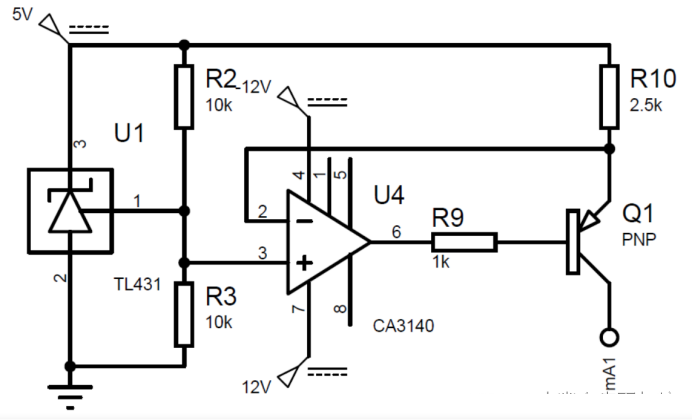
2.4 Nuolatinis srovės šaltinis
Dėl savaime įkaistančio terminio rezistoriaus efekto, it is necessary to ensure that the current flowing through the resistor is as small as possible, and generally the current is expected to be less than 10mA. Patikrinta, kad platinos rezistorius PT100 savaime įkaista 1 mW will cause a temperature change of 0.02 to 0.75℃, so reducing the current of the platinum resistor PT100 can also reduce its temperature change. Tačiau, jei srovė per maža, jis jautrus triukšmo trukdžiams, so it is generally taken at 0.5 į 2 Ma, todėl nuolatinės srovės šaltinio srovė pasirenkama kaip 1mA nuolatinės srovės šaltinis.
The chip selected is the constant voltage source chip TL431, and then the current negative feedback is used to convert it into a constant current source. Grandinė parodyta paveikslėlyje:
The operational amplifier CA3140 is used to improve the load capacity of the current source, o išėjimo srovės skaičiavimo formulė yra:
Insert picture description here The resistor should be a 0.1% tikslumo rezistorius. Galutinė išėjimo srovė yra 0,996 mA, tai yra, tikslumas yra 0.4%.
Nuolatinės srovės šaltinio grandinė turi turėti šias charakteristikas:
Temperatūros stabilumas: Kadangi mūsų temperatūros matavimo aplinka yra 0-100 ℃, srovės šaltinio išėjimas neturėtų būti jautrus temperatūrai. And TL431 has an extremely low temperature coefficient and low temperature drift.
Geras apkrovos reguliavimas: Jei srovės bangavimas yra per didelis, tai sukels skaitymo klaidas. Pagal teorinę analizę. Since the input voltage varies between 100-138.5mV, ir temperatūros matavimo diapazonas yra 0-100 ℃, temperatūros matavimo tikslumas yra ±1 laipsnis Celsijaus, todėl išėjimo įtampa turėtų pasikeisti 38,5/100 = 0,385 mV kas 1 ℃ aplinkos temperatūrai padidėjus. Siekiant užtikrinti, kad srovės svyravimai neturėtų įtakos tikslumui, apsvarstykite patį ekstremaliausią atvejį, adresu 100 laipsniai Celsijaus, PT100 varžos vertė turėtų būti 138,5R. Tada srovės pulsacija turėtų būti mažesnė nei 0,385/138,5 = 0,000278 mA, tai yra, the change in current during the load change should be less than 0.000278mA. Realiame modeliavime, dabartinis šaltinis iš esmės išlieka nepakitęs.
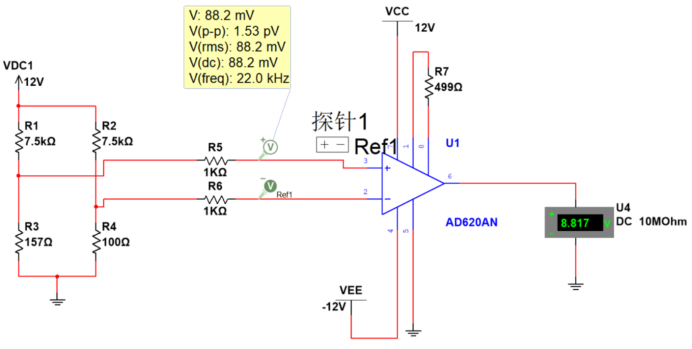
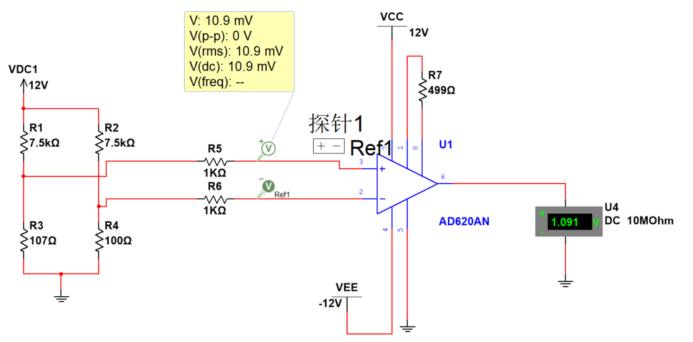
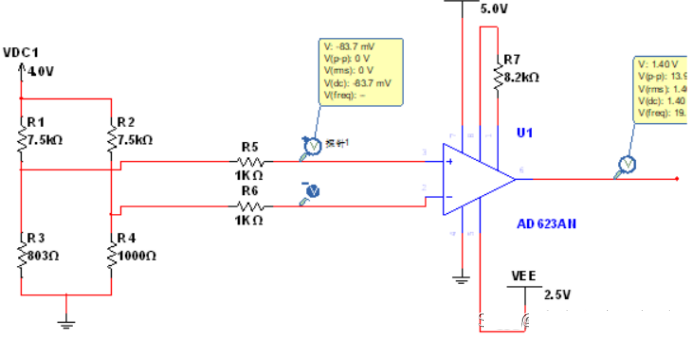
3. AD623 gavimo grandinės sprendimas
Principas gali būti susijęs su aukščiau nurodytu tilto matavimo principu.
Žemos temperatūros gavimas:
Aukštos temperatūros gavimas
Insert picture description here
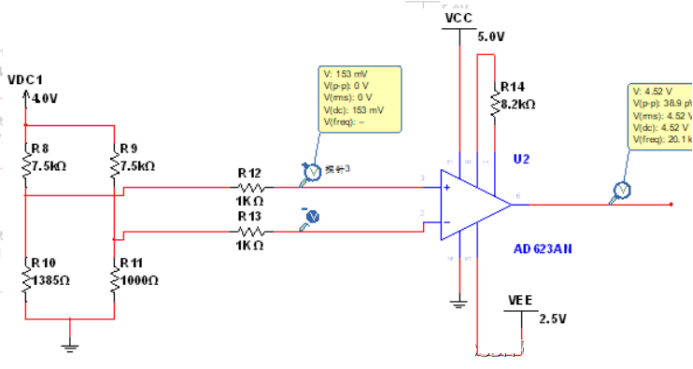
4. AD620 gavimo grandinės sprendimas
AD620 PT100 acquisition solution for high temperature (150°):
AD620 PT100 acquisition solution for low temperature (-40°):
AD620 PT100 acquisition solution for room temperature (20°):
5. Anti-interference filtering analysis of PT100 and PT1000 sensors
Temperatūros matavimas tam tikrame komplekse, atšiaurioje ar specialioje aplinkoje bus dideli trukdžiai, daugiausia įskaitant EMI ir REI. Pavyzdžiui, taikant variklio temperatūros matavimą, high-frequency disturbances caused by motor control and high-speed rotation of the motor.
Taip pat yra daug temperatūros kontrolės scenarijų aviacijos ir kosmoso transporto priemonėse, kurios matuoja ir valdo elektros ir aplinkos kontrolės sistemą. Temperatūros valdymo pagrindas yra temperatūros matavimas. Kadangi termistoriaus varža gali keistis tiesiškai priklausomai nuo temperatūros, Platinos atsparumo naudojimas temperatūrai matuoti yra efektyvus didelio tikslumo temperatūros matavimo metodas. Pagrindinės problemos yra tokios:
1. Švino laido varža lengvai įvedama, taip paveikdamas jutiklio matavimo tikslumą;
2. In certain strong electromagnetic interference environments, the interference may be converted into DC output offset error after being rectified by the instrument amplifier, turinčios įtakos matavimo tikslumui.
5.1 Oro erdvėlaivio PT1000 gavimo grandinė
Dėl antielektromagnetinių trukdžių tam tikroje aviacijoje žr. orlaivių PT1000 gavimo grandinės konstrukciją..
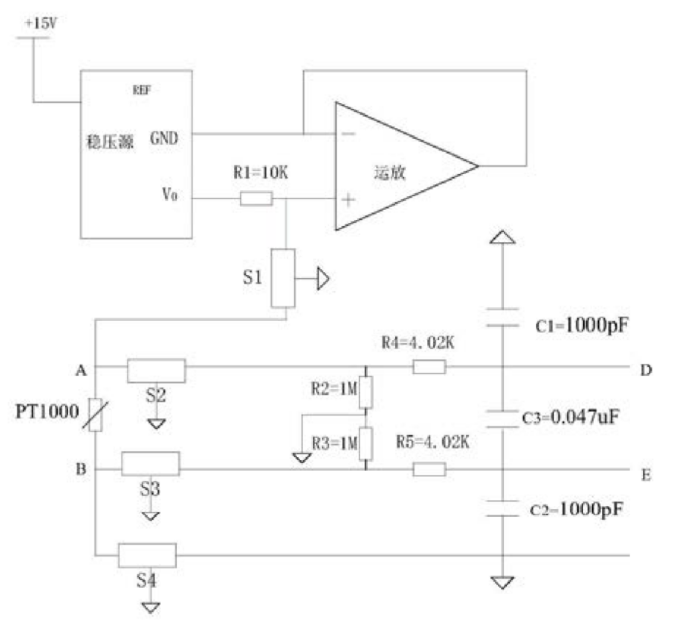
Filtras yra nustatytas atokiausiame gavimo grandinės gale. The PT1000 acquisition preprocessing circuit is suitable for anti-electromagnetic interference preprocessing of airborne electronic equipment interfaces; the specific circuit is:
+15V įėjimo įtampa per įtampos reguliatorių paverčiama +5V didelio tikslumo įtampos šaltiniu. The +5V high-precision voltage source is directly connected to the resistor R1, and the other end of the resistor R1 is divided into two paths. One is connected to the in-phase input end of the op amp, and the other is connected to the PT1000 resistor A end through the T-type filter S1. Operatyvinio stiprintuvo išėjimas yra prijungtas prie invertuojančios įvesties, kad susidarytų įtampos sekiklis, ir invertuojantis įėjimas yra prijungtas prie įtampos reguliatoriaus įžeminimo prievado, kad būtų užtikrinta, jog įtampa fazės įėjime visada būtų lygi nuliui. Praleidus S2 filtrą, vienas PT1000 rezistoriaus galas A padalintas į du kelius, one through resistor R4 as the differential voltage input D, ir vienas per rezistorių R2 į AGND. Praleidus S3 filtrą, kitas PT1000 rezistoriaus galas B yra padalintas į du kelius, one through resistor R5 as the differential voltage input E, ir vienas per rezistorių R3 į AGND. D ir E yra sujungti per kondensatorių C3, D yra prijungtas prie AGND per kondensatorių C1, ir E yra prijungtas prie AGND per kondensatorių C2. The precise resistance value of PT1000 can be calculated by measuring the differential voltage across D and E.
+15V įėjimo įtampa per įtampos reguliatorių paverčiama +5V didelio tikslumo įtampos šaltiniu. +5V yra tiesiogiai prijungtas prie R1. Kitas R1 galas yra padalintas į du kelius, vienas prijungtas prie operatyvinio stiprintuvo fazės įvesties, and the other connected to the A end of the PT1000 resistor through the T-type filter S1. Operatyvinio stiprintuvo išėjimas yra prijungtas prie invertuojančios įvesties, kad susidarytų įtampos sekiklis, ir invertuojantis įėjimas yra prijungtas prie įtampos reguliatoriaus įžeminimo prievado, kad būtų užtikrinta, jog įtampa invertuojamajame įėjime visada būtų lygi nuliui. Šiuo metu, srovė, tekanti per R1, yra pastovi 0,5 mA. Įtampos reguliatorius naudoja AD586TQ/883B, o operacinės sistemos stiprintuvas naudoja OP467A.
Praleidus S2 filtrą, vienas PT1000 rezistoriaus galas A padalintas į du kelius, vienas per rezistorių R4 kaip diferencinės įtampos įvesties galas D, ir vienas per rezistorių R2 į AGND. Praleidus S3 filtrą, kitas PT1000 rezistoriaus galas B yra padalintas į du kelius, vienas per rezistorių R5 kaip diferencinės įtampos įvesties galas E, ir vienas per rezistorių R3 į AGND. D ir E yra sujungti per kondensatorių C3, D yra prijungtas prie AGND per kondensatorių C1, ir E yra prijungtas prie AGND per kondensatorių C2.
R4 ir R5 varža yra 4,02k omų, R1 ir R2 varža yra 1M omų, C1 ir C2 talpa yra 1000pF, o C3 talpa yra 0,047 uF. R4, R5, C1, C2, ir C3 kartu sudaro RFI filtrų tinklą. The RFI filter completes the low-pass filtering of the input signal, and the objects filtered out include the differential mode interference and common mode interference carried in the input differential signal. Įvesties signale perduodamų bendrojo režimo trukdžių ir diferencinio režimo trukdžių –3dB ribinio dažnio apskaičiavimas parodytas formulėje:
Atsparumo vertės pakeitimas skaičiavime, bendrojo režimo ribinis dažnis yra 40 kHz, ir diferencinio režimo ribinis dažnis yra 2,6 KHZ.
Pabaigos taškas B yra prijungtas prie AGND per S4 filtrą. Tarp jų, visi filtro įžeminimo gnybtai nuo S1 iki S4 yra prijungti prie orlaivio ekranavimo įžeminimo. Kadangi srovė, tekanti per PT1000, yra žinoma 0,05 mA, tikslią PT1000 varžos vertę galima apskaičiuoti išmatuojant skirtingą įtampą abiejuose D ir E galuose.
Nuo S1 iki S4 naudojami T tipo filtrai, modelis GTL2012X-103T801, with a cutoff frequency of M±20%. Ši grandinė įveda žemųjų dažnių filtrus į išorinės sąsajos linijas ir atlieka RFI filtravimą pagal diferencinę įtampą. Kaip PT1000 išankstinio apdorojimo grandinė, efektyviai pašalina elektromagnetinius ir RFI spinduliuotės trukdžius, o tai labai pagerina surinktų vertybių patikimumą. Be to, įtampa tiesiogiai matuojama iš abiejų PT1000 rezistoriaus galų, pašalinant laidų pasipriešinimo sukeltą klaidą ir pagerinant varžos vertės tikslumą.
5.2 T tipo filtras
Insert picture description here
T tipo filtras susideda iš dviejų induktorių ir kondensatorių. Abu jo galai turi didelę varžą, ir jo įterpimo nuostolių efektyvumas yra panašus į π tipo filtro, bet tai nėra linkusi “skambėjimas” ir gali būti naudojamas perjungimo grandinėse.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt