Produktų kategorijos
- Šilumos saugiklis 32
- Paviršiaus laikikliai 12
- Termistorius 36
- PCB kalno saugiklių laikiklis 27
- Laidų diržai 6
- Ašmenų saugiklių laikikliai 17
- Termostatas 50
- Elektrinis saugiklis 24
- Automobilių temperatūros jutiklis 7
- Šilumos grandinės pertraukiklis 22
- „Fuse Box Holder“ 36
- Temperatūros jutiklis 75
- Šiluminis jungiklis 68
- Automobilių saugiklis 20
- Varžtas žemyn 8
Produktų žymos
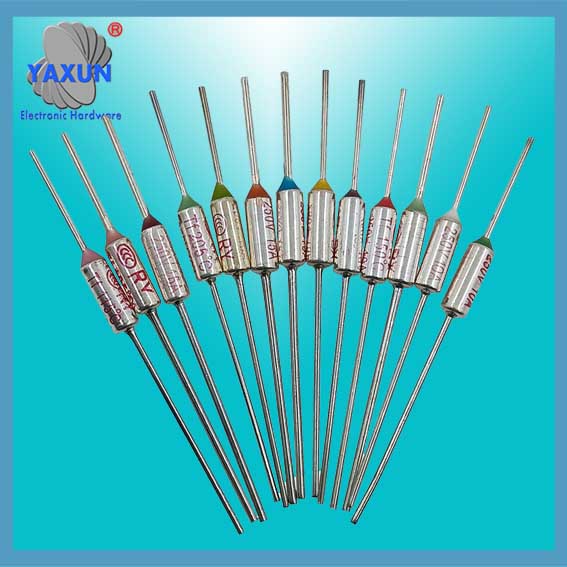
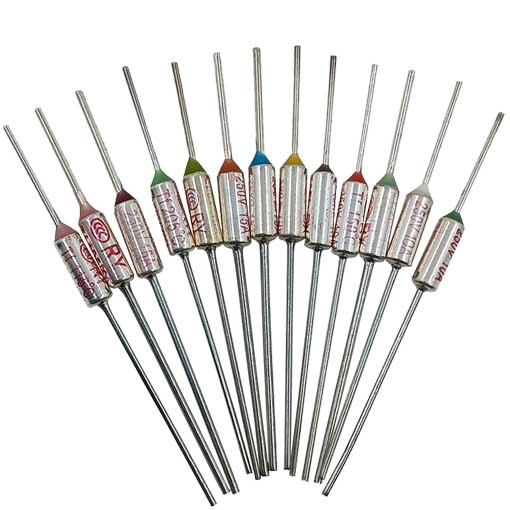
Tamura/NEC SF metalinis korpusas 15A Temperatūros saugiklis
AUPO veikimo principas / Tamura / NEC SF terminis saugiklis yra pagrįstas medžiagos šiluminio plėtimosi ir laidumo savybėmis. Kai temperatūra grandinėje pakyla iki vardinės saugiklio suveikimo temperatūros, metalinė saugiklio medžiaga dėl karščio išsiplės. Kai šis išsiplėtimas pasiekia tam tikrą laipsnį, dėl to stipriai padidės varža saugiklio viduje.
AUPO veikimo principas / Tamura / NEC SF terminis saugiklis yra pagrįstas medžiagos šiluminio plėtimosi ir laidumo savybėmis. Kai temperatūra grandinėje pakyla iki vardinės saugiklio suveikimo temperatūros, metalinė saugiklio medžiaga dėl karščio išsiplės. Kai šis išsiplėtimas pasiekia tam tikrą laipsnį, dėl to stipriai padidės varža saugiklio viduje. The increase in resistance will cause the fuse to heat up rapidly, further accelerating the expansion of the metal material. When the expansion reaches a certain degree, the fuse will disconnect in the circuit, thereby protecting the circuit and equipment from damage due to overheating.
Under normal circumstances, when the current passes through the thermal fuse, the fuse will maintain a low resistance state and will not affect the circuit.
When overheating occurs in the circuit, the thermal fuse begins to work. Its metal material expands due to heat, causing the resistance inside the fuse to change.
As the resistance rises, the fuse temperature rises further, accelerating the expansion of the metal material.
When the metal material expands to a certain extent, the resistance inside the fuse will rise sharply, causing the current in the circuit to be cut off.
After the fuse is disconnected, a new fuse needs to be replaced to restore the normal operation of the circuit. This is because it is difficult for the metal material to return to its original state after expansion, so that the resistance always remains high.
2. Structural features
Thermal fuse is a temperature sensing circuit cutting device with the characteristic of one-time fusing, tai yra, it only acts once at the fusing temperature and cannot be used again. Common types of thermal fuses include organic thermal fuses and alloy thermal fuses.
Taking the organic thermal fuse as an example, its structural features mainly include components such as temperature sensing block, compression spring and star spring. Kai temperatūra aplink organinį šiluminį saugiklį pakyla iki jo darbinės temperatūros, the temperature sensing block will melt, and the compression spring will relax to make room, so that the star spring is pushed away to contact the pin, taip atjungiant srovės kelią. Tokiu būdu, the circuit will be permanently cut off.
Product Features of Thermal Fuse
SEFUSE temperature fuse installation precautions:
1. Naudojant švino lenkimą, it should be bent from a part more than 6 mm from the root; Kai lenkiasi, do not damage the roots and leads, and do not pull, paspauskite, or twist the leads forcibly.
2. Kai šiluminis saugiklis tvirtinamas varžtais, riveting or binding posts, it should be able to prevent mechanical creep and poor contact.
3. The connecting parts should be able to work reliably within the working range of the electrical product without displacement due to vibration and shock.
4. When welding the lead wire, the heating humidity should be limited to a minimum, and no high temperature should be applied to the thermal fuse; Do not forcibly pull, paspauskite, or twist the thermal fuses and leads; after soldering, cool down immediately for more than 30 sekundžių.
5. The thermal fuse can only be used under the conditions of the specified rated voltage, current and specified temperature. Pay particular attention to the maximum continuous temperature that the thermal fuse can withstand.
PASTABA: Nominal current, lead length and temperature can be designed according to customer requirements.
LE series Thermal Fuse (15A)
Produkto savybės
Naudojant temperatūros saugiklio metalinį korpusą ir temperatūros jutimo organines daleles.
Priklausantys neatkuriamo tipo šiluminiai saugikliai. Išsilydo temperatūros saugiklis, net jei aplinkos temperatūra nukrenta, jis nebus įjungtas.
Nėra švino (Pb) ir kadmis (Cd), ir atitinka RoHS.
REACH nenurodyta 46 SVHC kategorijos (SVHC).
Produkto dydis
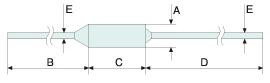
250V 15A Temperature fuse
| Kabelio ilgis | Matmenys (mm) | ||||
| A | B | C | D | E | |
| Standartinis LE | 4.0±0,1 | 20±3 | 10.1±3 | 35±3 | 1.0±0,1 |
| Ilgas LE(L) | 4.0±0,1 | 38±3 | 10.1±3 | 35±3 | 1.0±0,1 |
| Modelis | Nominali temperatūra Tf (℃) |
Darbinė temperatūra (℃) |
Nominali srovė (A) |
Nominali įtampa (V) |
palaikant temperatūrą Th(℃) |
Maksimali temperatūros riba Tm (℃) |
| LE070 | 73 | 71±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 50 | 150 |
| LE073 | 77 | 74±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 50 | 150 |
| LE080 | 84 | 80±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 50 | 150 |
| LE090 | 94 | 91+3/-2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 65 | 150 |
| LE095 | 99 | 95±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 71 | 150 |
| LE108 | 113 | 109±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 85 | 150 |
| LE117 | 121 | 117±3 | 15.0 | AC250 | 95 | 160 |
| LE124 | 128 | 124±3 | 15.0 | AC250 | 102 | 160 |
| LE128 | 133 | 129+3/-2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 105 | 160 |
| LE138 | 142 | 138±3 | 15.0 | AC250 | 110 | 160 |
| LE152 | 157 | 152±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 130 | 175 |
| LE169 | 172 | 167±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 145 | 190 |
| LE189 | 192 | 189±3 | 15.0 | AC250 | 165 | 300 |
| LE213 | 216 | 213±2 | 15.0 | AC250 | 190 | 300 |
Susisiekite su mumis
Laukiu jūsų el. Pašto, Mes jums atsakysime 12 Valandos su vertinga informacija, kurios jums reikėjo.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt


