製品カテゴリ
- 温度ヒューズ 32
- 表面実装ヒューズ 12
- サーミスター 36
- PCB マウント ヒューズ ホルダー 27
- ワイヤハーネス 6
- ブレードヒューズホルダー 17
- サーモスタット 50
- 電気ヒューズ 24
- 自動車温度センサー 7
- サーマルサーキットブレーカー 22
- ヒューズボックスホルダー 36
- 温度センサー 75
- サーマルスイッチ 68
- カーヒューズ 20
- ボルトダウンヒューズ 8
製品タグ
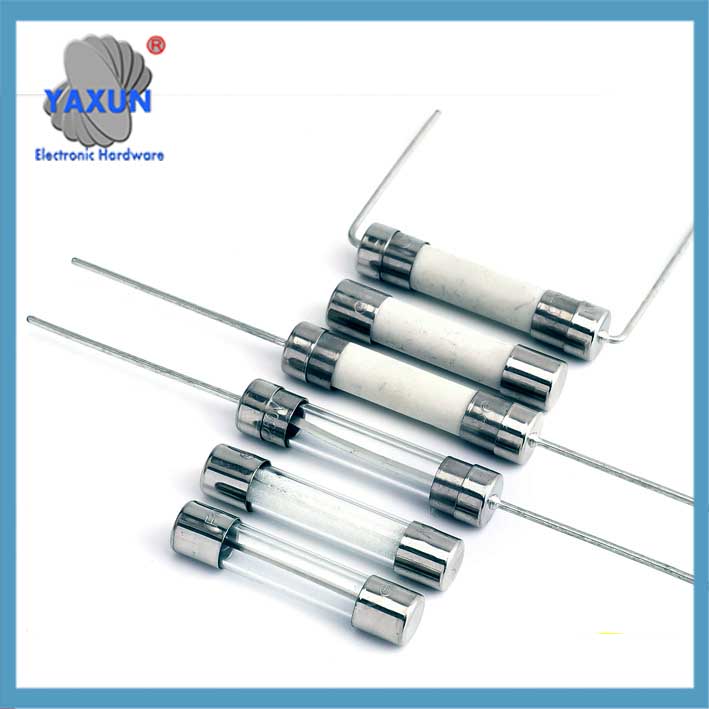
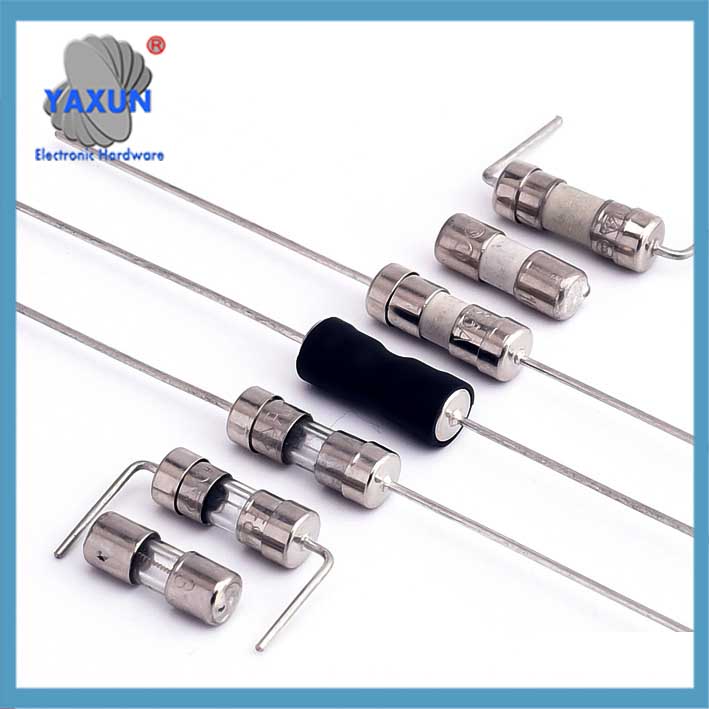
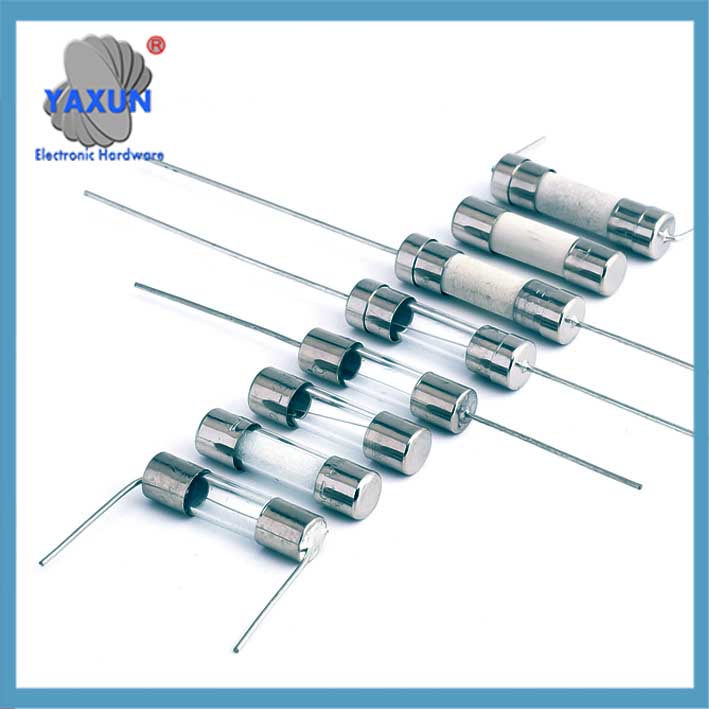
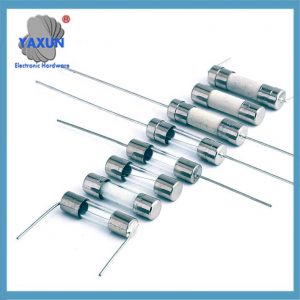
過電流保護 | 5×20 6×30 mm カートリッジヒューズ
過電流保護電気ヒューズは、電流が所定のレベルを超えたときに回路内の電気の流れを遮断する安全装置です。. 犠牲的なリンクとして機能します, 回路を溶かして遮断し、過熱による配線やその他のコンポーネントの損傷、または過剰な電流による火災の可能性を防ぎます。.
Overcurrent protection electrical fuse is a circuit protection device that cuts off abnormal current through a fusing mechanism. Its core function is to fuse when the current exceeds the rated value to protect the back-end equipment. The following is a detailed explanation of the classification and characteristics:
Traditional fuse type fuse
working原則:
When the current exceeds the limit, the metal melt melts due to the Joule heat effect and disconnects the circuit, which is a one-time protection device. The typical response time is in milliseconds, and short-circuit protection requires fast fusing (such as the glass tube fuse fusing time ≤40ms) . Fusible Link:
A fuse contains a small, conductive wire or strip (the fusible link) designed to melt or vaporize when the current flowing through it exceeds its rated capacity.
過電流保護:
This melting action opens the circuit, interrupting the flow of electricity and preventing further damage.
Single-Use:
Fuses are designed for one-time use and must be replaced after they interrupt the circuit.
信頼性: Fuses are known for their reliability in interrupting overcurrents.
Cost-effectiveness: They are generally inexpensive compared to other overcurrent protection devices.
Simplicity: The design is simple, making them easy to understand and use.
Variety: Fuses come in various sizes, shapes, and current ratings to suit different applications.
種類: Fuses are categorized into different classes (例えば, L, RK1, RK5, T, J, CC, 等) to address specific overcurrent scenarios and performance requirements.
Types and Structures Plug-in type: commonly used in automotive circuits, current 1-120A, divided into four specifications from ultra-small to large.
SMD type: SMDパッケージング, 高密度PCBに最適, containing quartz sand arc extinguishing medium.
Glass tube type: transparent shell is convenient for observing the fuse status, current 0.5-80A.
Key parameters Rated current/voltage: such as 250V/10A slow-break type, it needs to be derated according to 75% (UL標準) または 90% (IEC standard) of the actual current.
Fusing characteristics: fast-break type (anti-short circuit) and slow-break type (anti-surge).
When are fuses used?
Branch circuits:
Fuses are commonly used in household and commercial electrical systems to protect individual circuits.
Equipment protection:
They can be used to protect specific components within a device, such as transformers or circuit boards.
Time-delay and fast-acting:
Fuses can be designed for time-delay applications (例えば, for inductive loads with high inrush currents) or fast-acting applications (例えば, for resistive loads).
Self-resettable fuse (PPTC) Action mechanism
Made of high molecular polymer and conductive particles, the resin expands due to heat when overcurrent occurs, blocking the path, and cools down to restore low resistance after the fault is eliminated1011. The response speed is inversely proportional to the current intensity (のような 0805 package second-level protection).
Compared with traditional fuses
| 特徴 | PPTC | Traditional fuse |
|---|---|---|
| Resilience | 自動リセット | Requires manual replacement |
| 内部抵抗 | 低抵抗 (starting from 0.008Ω) | Lower (milliohm level) |
| 該当するシナリオ | Hot-swap interface, battery protection | High reliability power input |
Examples of Overcurrent Scenarios:
Short circuits:
When two or more conductors come into direct contact, creating a low-resistance path for current, a short circuit occurs.
Overloads:
When a circuit is subjected to a current higher than its capacity for an extended period, it’s considered an overload.
Ground faults:
When electricity flows from a live wire to ground (earth), it’s called a ground fault.
Arc faults:
These are dangerous electrical discharges that can occur in wiring or electrical components.
Limitations:
交換: Fuses require replacement after they blow, which can be inconvenient.
Not resettable: Unlike circuit breakers, fuses cannot be reset and reused.
May not be as precise: Fuses may not offer the same level of precision in interrupting currents as some circuit breakers.
In conclusion, fuses are a vital part of electrical safety, providing a reliable and cost-effective way to protect circuits and equipment from the dangers of overcurrents.
お問い合わせ
メールを待っています, 以内に返信させていただきます 12 必要な貴重な情報を何時間も入手できる.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt