Categorías de Producto
- fusible térmico 32
- fusibles de montaje en superficie 12
- termistor 36
- Portafusibles de montaje en PCB 27
- Arnés de cableado 6
- Portafusibles de cuchilla 17
- termostato 50
- Fusible eléctrico 24
- Sensor de temperatura automotriz 7
- Disyuntor térmico 22
- Portafusibles 36
- Sensor de temperatura 75
- Interruptor térmico 68
- Fusible del coche 20
- Fusibles atornillados 8
Etiquetas de productos
Termistor PTC compuesto para transformadores, Potencia de conmutación
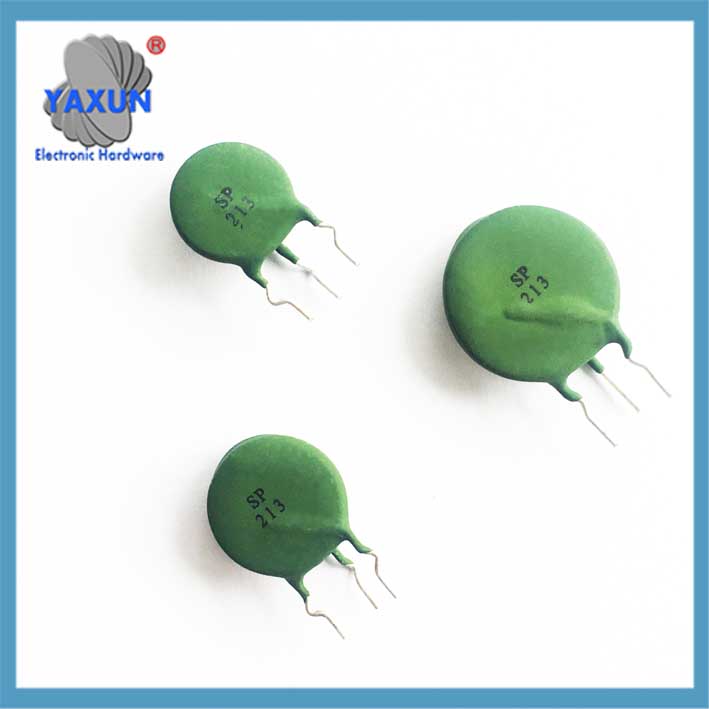
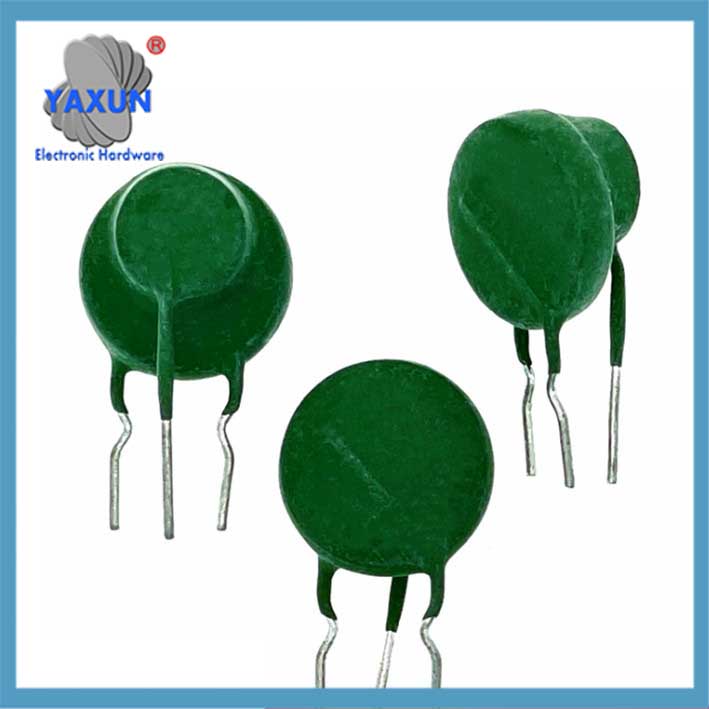
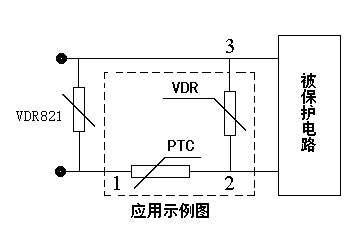
Un termistor PTC compuesto utiliza una combinación térmica acoplada, ajustado y encapsulando un varistor VDR y un termistor PTC. Se utiliza principalmente en el cambio de alimentación y los circuitos primarios del transformador en medidores de potencia y otras fuentes de alimentación, proporcionando protección integral de corriente y voltaje.
Un termistor PTC compuesto es un componente electrónico que combina un coeficiente de temperatura positivo (PTC) características con protección contra sobretensiones, Se utiliza principalmente para protección dual contra sobrecorriente y sobretensión.. Un termistor PTC compuesto utiliza una combinación térmica acoplada, ajustado y encapsulando un varistor VDR y un termistor PTC. Se utiliza principalmente en el cambio de alimentación y los circuitos primarios del transformador en medidores de potencia y otras fuentes de alimentación, proporcionando protección integral de corriente y voltaje. Esto resuelve las dificultades asociadas con el uso de un solo termistor PTC con transformadores.. Es posible que los instrumentos y equipos protegidos por un termistor PTC no funcionen correctamente en condiciones de sobretensión o sobrecorriente., y los instrumentos de baja temperatura pueden no estar protegidos por el PTC cuando ocurren anomalías.
El siguiente es un análisis de sus características y aplicaciones principales.:
I. Estructura y principio
Composición de materiales: Normalmente hecho de una resina de poliolefina., polietileno, o matriz de resina epoxi, Se incorporan partículas conductoras como negro de carbón y óxido de vanadio.. A temperatura ambiente, Las partículas conductoras forman cadenas conductoras continuas., dando como resultado una baja resistividad. Cuando la temperatura aumenta hasta el punto de fusión del polímero., la matriz se expande, rompiendo las cadenas conductoras y provocando un aumento repentino de la resistividad (efecto PTC). Diseño compuesto: Algunos modelos integran un termistor PTC y un varistor (VDR) en un solo paquete, logrando protección dual contra sobrecorriente y sobretensión a través del acoplamiento térmico. Por ejemplo, durante un evento de sobretensión, El varistor absorbe energía y genera calor., provocando un salto en la resistencia del PTC, limitar la corriente y reducir el voltaje mediante 4%.
II. Características de rendimiento
RELACIÓN ASCENSO-RESISTENCIA: La resistencia puede variar según 5-10 órdenes de magnitud dentro de un estrecho rango de temperatura, haciéndolo adecuado como elemento de interruptor térmico.
RESPONSABILIDAD: Después de la actuación, tarda mucho en enfriarse antes de volver a su estado inicial, resultando en una respuesta lenta.
AUTORECUPERACIÓN: Vuelve automáticamente a un estado de baja resistencia después de que se resuelve la falla, eliminando la necesidad de reemplazo.
III. Aplicaciones típicas
Electrodomésticos e Industriales: Se utiliza para protección contra sobrecorriente en equipos como calentadores de agua eléctricos., motores, y transformadores.
Medidores de potencia: Proporciona protección combinada contra sobretensión y sobrecorriente en medidores inteligentes y fuentes de alimentación conmutadas..
Electrónica automotriz: Se utiliza en aplicaciones de monitoreo de temperatura, como control de motores y sistemas de aire acondicionado..
Cuando un varistor absorbe grandes cantidades de energía, se calentará. Debido al acoplamiento térmico, la temperatura del termistor PTC también aumenta. Además, el termistor se calienta debido al aumento de corriente. Cuando la temperatura alcanza la temperatura de conmutación del termistor PTC, su resistencia salta, y la corriente disminuye bruscamente. Simultáneamente, la caída de voltaje a través del termistor aumenta significativamente, reduciendo el voltaje a través del varistor y permitiendo que solo fluya una pequeña corriente de fuga. Esto reduce el voltaje del circuito protegido dentro del rango de voltaje de funcionamiento normal., Permitir que el medidor de potencia funcione normalmente..
IV. Parámetros de selección
Los siguientes parámetros deben ser considerados durante la selección.:
Corriente de funcionamiento (Él) y corriente no operativa (yo);
Curie temperatura (tc, normalmente 115±7°C);
voltaje del varistor (V) y tensión máxima de funcionamiento (Vmáx).
Modelos comunes de termistores compuestos.
| Modelo | Curie | Actuando | No actuante | varisor | Clasificación | Dimensiones | |
| Temperatura | Actual | Actual | Voltaje | Funcionamiento máximo | |||
| (25 ℃) | (60 ℃) | (25 ℃) | Voltaje | ||||
| Tc(℃) | Él(mamá) | yo(mamá) | V(V) | Vmáx(V) | Dmáx. | Hmáx. | |
| SPMZB-10S300-500RM/14D900 | 115±7 | 250 | 70 | 90 | 65 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S300-600RM/14D121 | 115±7 | 200 | 60 | 120 | 65 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S400-800RM/14D181 | 115±7 | 200 | 50 | 180 | 120 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-10S300-500RM/14D181 | 115±7 | 250 | 70 | 180 | 120 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-06S900-161RM/10D391 | 115±7 | 150 | 30 | 390 | 265 | 12 | 8 |
| SPMZB-06S151-251RM/10D391 | 115±7 | 120 | 25 | 390 | 265 | 12 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S400-800RM/12D391 | 115±7 | 200 | 50 | 390 | 265 | 14 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S600-121RM/12D391 | 115±7 | 180 | 40 | 390 | 265 | 14 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S600-121RM/14D391 | 115±7 | 180 | 40 | 390 | 265 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-08S800-161RM/14D391 | 115±7 | 160 | 35 | 390 | 265 | 16 | 8 |
| SPMZB-10S300-500RM/14D391 | 115±7 | 250 | 90 | 390 | 265 | 16 | 10 |
| SPMZB-10S400-800RM/14D391 | 115±7 | 220 | 70 | 390 | 265 | 16 | 10 |
| SPMZB-10S400-800RM/14D471 | 115±7 | 220 | 70 | 470 | 330 | 16 | 10 |
| SPMZB-16S200-300RM/20D391 | 115±7 | 450 | 130 | 390 | 265 | 22 | 10 |
Contáctenos
Esperando tu email, le responderemos dentro de 12 horas con la valiosa información que necesitabas.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt