Categories de productes
- fusible tèrmic 32
- Fustes de muntatge superficial 12
- termistor 36
- Suport de fusibles de muntatge de PCB 27
- Arnès de cablejat 6
- Titulars de fusibles de fulla 17
- termòstat 50
- Fusible elèctric 24
- Sensor de temperatura de l’automoció 7
- Interruptor de circuit tèrmic 22
- Fuse Box-titure 36
- Sensor de temperatura 75
- Interruptor tèrmic 68
- Fusible del cotxe 20
- Fustes de forrellat 8
Etiquetes de producte
Funcions i aplicacions dels fusibles electrònics (eFuses)
Fusibles electrònics (eFuses) Són dispositius d'estat sòlid que protegeixen els circuits electrònics de condicions de sobreintensitat. A diferència dels fusibles tradicionals, es poden reiniciar electrònicament, oferint una solució més còmoda i eficient per a la protecció del circuit. eFuses protegeixen contra curtcircuits, sobrecàrregues, i altres condicions de falla, evitant danys als dispositius i al cablejat.
A efuse (also called a efuse link) is an electronic component used to protect a circuit from overcurrent or overheating. Its core function is to automatically blow in abnormal situations to cut off the circuit. The following are its key points:
jo. Core Principle and Structure
Principi de funcionament
When the current rises abnormally, the conductor heats up due to resistance (following the formula Q=I2RTQ=I2RT), and when it reaches the melting point of the melt material, it melts automatically, tallant així el circuit.
Basic Structure
Melt Material: Lead-antimony alloy (punt de fusió baix, high resistivity) was used in the early days, and silver, copper or special alloys are mostly used in modern times.
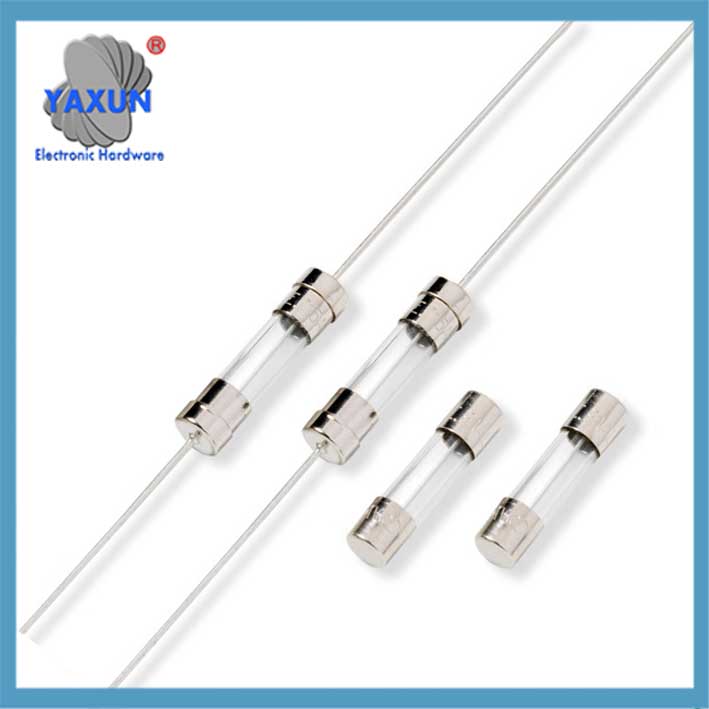
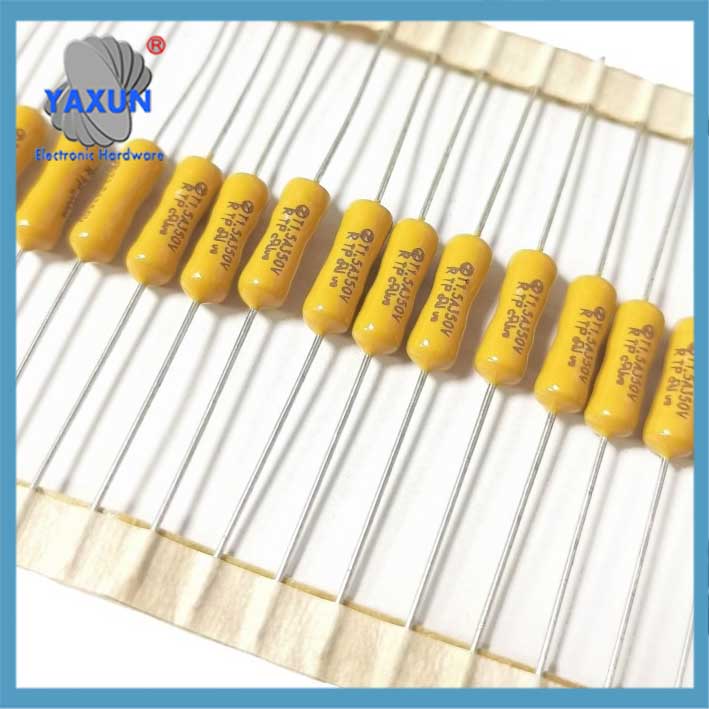
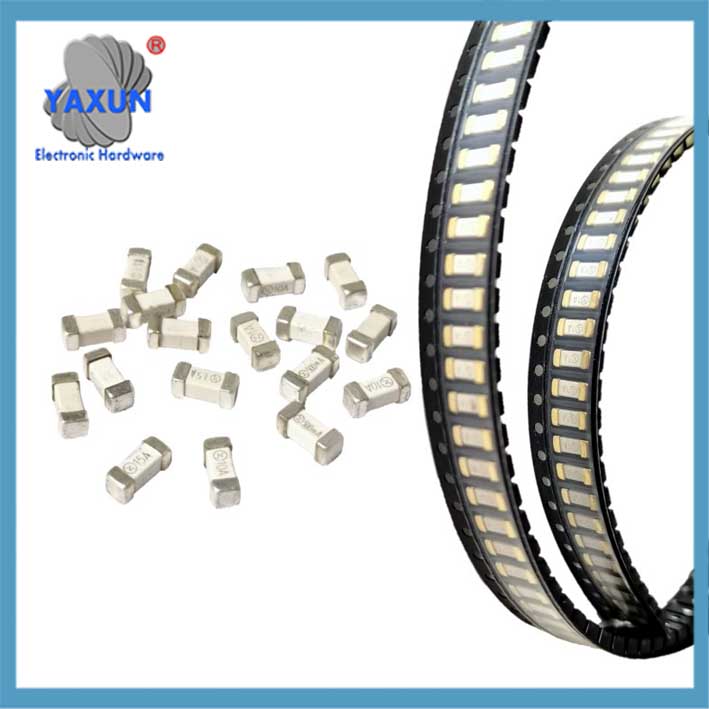
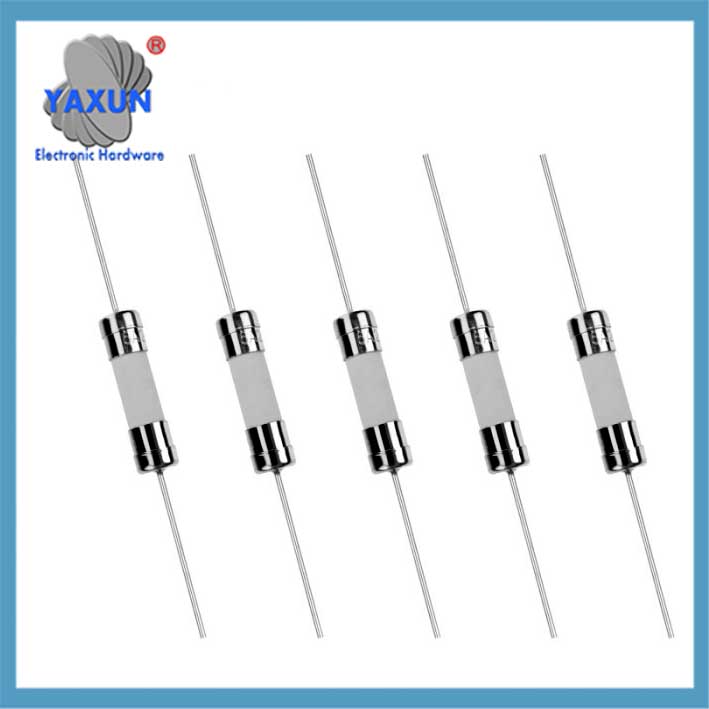
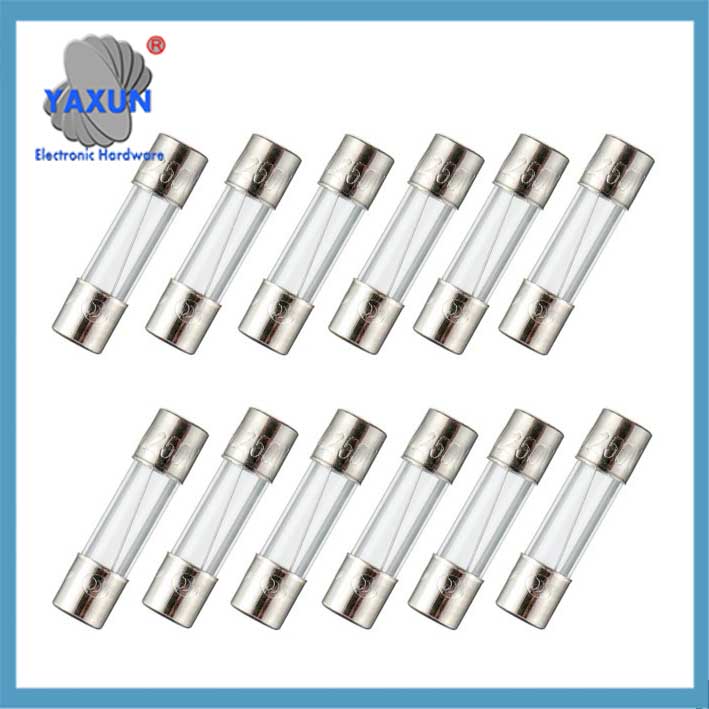
Packaging Form: Including glass tubular (such as 5×20mm, 6×32mm, 3.6×10mm), ceramic tubular, sheet (for automobiles), SMD patch type, etc.
Protecció contra sobreintensitat:
eFuses interrupt the flow of current when it exceeds a predetermined threshold, preventing damage to sensitive electronic components.
Short Circuit Protection:
They quickly detect and interrupt short circuits, which are low-resistance paths that cause excessive current flow.
Protecció de sobrecàrrega:
eFuses safeguard against prolonged overcurrent conditions, such as those caused by a mismatched load.
Fault Detection and Isolation:
They can be designed to detect and isolate various fault conditions, including inrush currents, sobretensió, reverse current, and reverse polarity.
Reinicialització automàtica:
Many eFuses can be reset electronically, allowing them to return to normal operation after a fault condition is cleared, eliminating the need for physical replacement.
Adjustable Slew Rate:
Some eFuses offer adjustable slew rates, allowing for control over the speed at which the current rises, which can be useful in preventing damage from inrush currents.
III. Classification and Application Scenarios
| Type | Característiques | Typical applications |
|---|---|---|
| Fast-blow type | Extremely fast response (<0.001 segons), used in sensitive circuits | Semiconductor equipment, precision electronic products |
| Slow-blow type | Allows short-term overload (0.01–0.1 seconds to blow), surge current resistance | Motor starting circuit, adaptador de corrent |
| Temperature fuse | Inductive overheating, single-use | Heating appliances such as hair dryers and rice cookers |
| High-voltage fuse | Includes mounting components (such as clamping springs) to simplify pipe connection | High-voltage power system |
Applications of Electronic Fuses:
Electrònica d'automoció:
eFuses are used in various automotive systems, including engine control units, infotainment systems, and safety systems.
Automatització industrial:
They are utilized in programmable logic controllers (PLCs), motor control systems, and other industrial automation equipment.
Electrònica de consum:
eFuses are found in smartphones, portàtils, tablets, and other portable devices.
Data Centers:
They are used in power distribution units and server racks to protect critical infrastructure.
Hot-Swap Systems:
eFuses provide protection in systems where components can be added or removed while the system is running.
Battery Management Systems:
They are used in battery charging and discharging circuits to prevent overcurrent and overvoltage conditions.
Power Distribution:
eFuses are used in power distribution units and power supplies to protect against overcurrents and short circuits.
General Circuit Protection:
eFuses can be used in any electronic circuit where overcurrent protection is needed.
III. Key usage specifications
Prohibited substitution of materials
Copper wire or iron wire cannot be used as a substitute (low resistivity, high melting point), which may cause an accident due to failure to blow in time.
Factors de selecció
Corrent nominal: It needs to be slightly higher than the maximum working current of the circuit (such as 6A fuse for 5A circuit).
Capacitat de ruptura: It must be greater than the maximum short-circuit current of the circuit (such as 100A short circuit, ≥100A breaking capacity).
Ambient temperature: Derating is required for high temperature environment.
IV. Technological progress
Automated detection: Such as material transfer components + machine vision detection device, to improve the efficiency of fuse production and sorting.
Structural optimization: High-voltage fuses adopt a clamping spring design to simplify the installation process.
Nota: After the fuse is blown, it needs to be replaced with a new product of the same specification. For glass tube models, the fuse status can be visually observed to determine whether it is invalid.
Poseu -vos en contacte amb nosaltres
Esperant el vostre correu electrònic, Us respondrem dins 12 hores amb informació valuosa que necessiteu.
 English
English Afrikaans
Afrikaans العربية
العربية বাংলা
বাংলা bosanski jezik
bosanski jezik Български
Български Català
Català 粤语
粤语 中文(简体)
中文(简体) 中文(漢字)
中文(漢字) Hrvatski
Hrvatski Čeština
Čeština Nederlands
Nederlands Eesti keel
Eesti keel Suomi
Suomi Français
Français Deutsch
Deutsch Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά हिन्दी; हिंदी
हिन्दी; हिंदी Magyar
Magyar Bahasa Indonesia
Bahasa Indonesia Italiano
Italiano 日本語
日本語 한국어
한국어 Latviešu valoda
Latviešu valoda Lietuvių kalba
Lietuvių kalba македонски јазик
македонски јазик Bahasa Melayu
Bahasa Melayu Norsk
Norsk پارسی
پارسی Polski
Polski Português
Português Română
Română Русский
Русский Cрпски језик
Cрпски језик Slovenčina
Slovenčina Slovenščina
Slovenščina Español
Español Svenska
Svenska ภาษาไทย
ภาษาไทย Türkçe
Türkçe Українська
Українська اردو
اردو Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt